Introduction
As organizations move AI from experiments to production, AI infrastructure bottlenecks appear before model quality becomes a concern. These hidden issues are a major reason why enterprise AI projects fail at scale.
To scale faster, teams invest largely in AI infrastructure. Gartner estimates that global AI infrastructure spending will reach $1.74 trillion by 2027. Much of this spend goes into GPUs, but adding more hardware increases costs without solving root causes.
Despite massive investment, performance issues persist due to GPU utilization issues, fragile data pipelines, mixed training and inference workloads, and limited AI-specific observability.
This blog explains where AI infrastructure breaks and how to fix it at the system level.
Understanding AI Infrastructure Beyond Compute
AI infrastructure is a set of systems that support building, training, deploying, and running AI models at scale. It includes GPUs, data movement, storage, networking, orchestration, and monitoring to deliver consistent performance in production.
Types of AI Infrastructure
Here are different kinds of AI infrastructure:
On-prem vs Cloud AI Infrastructure
On-prem data center offers full control and predictable performance. In contrast, cloud infrastructure provides on-demand access to compute without upfront investment.
- Choose on-prem for regulated, steady workloads
- Choose cloud for experimentation and fast scaling
The choice depends on how much control, compliance, and cost predictability your AI workloads require versus flexibility and speed.
Hybrid vs Multi-tenant AI Infrastructure
Hybrid AI infrastructure splits workloads across on-premises and cloud environments. Conversely, multi-tenant shares the same AI platform and GPUs across multiple teams or users.
- Choose hybrid to maintain control and scalability
- Choose multitenant to maximize resource utilization and reduce per-team costs
Selecting between hybrid and multi-tenant models comes down to maintaining governance needs with shared use of AI resources.
Why AI Infrastructure Matters?
Weak infrastructure leads to slow training, unstable inference, and high costs. Poor infrastructure also introduces AI lifecycle constraints that disrupt data preparation, model training, deployment, and ongoing operations.
With a strong AI infrastructure, you can ensure models train faster, serve predictions reliably, and scale without wasting resources.
What Are the Biggest AI infrastructure bottlenecks and How to Fix Them?
Since infrastructure components are interconnected, a slowdown in other parts of the pipeline affects the entire AI system and degrades performance. These hidden infrastructure issues are a major reason why enterprise AI projects fail at scale.
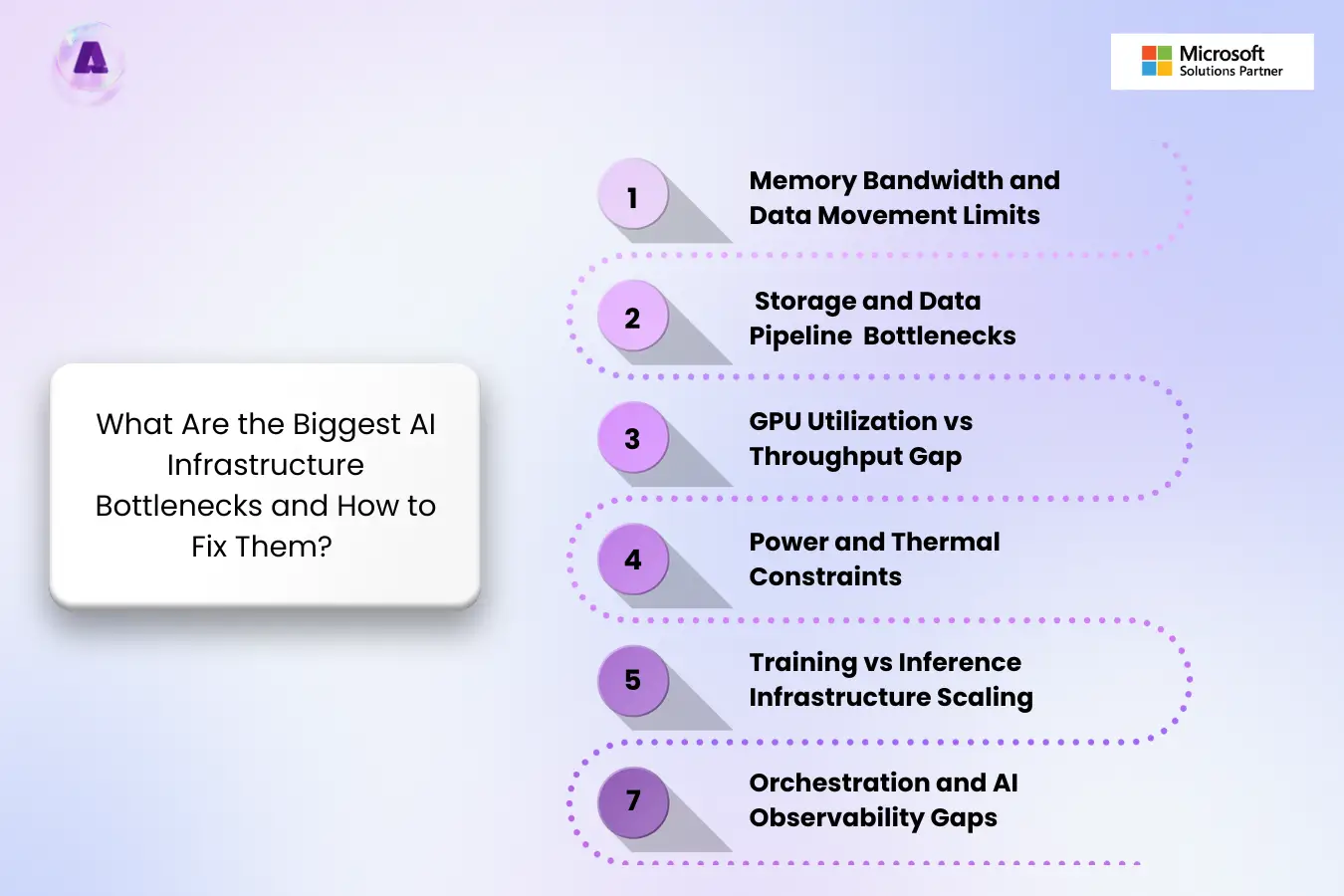
Below are the GPU bottlenecks in AI infrastructure you should watch for and fix early.
1. Memory Bandwidth and Data Movement Limits
When memory cannot supply data to GPU quickly, the system slows training and inference even though compute capacity is available.
Why this happens
- Large models exceed memory wall
- High-bandwidth memory (HBM) supply shortages
- Poor cache reuse
- Inefficient paging
- Context inflation while reading long documents
Why this matters
- RAM overflows
- Difficult to scale capacity linearly
- Unmanageable token sizes
How to fix it
- Utilize distillation and quantization to reduce model size and fit more models into available memory
- Track tokens per second and memory throughput regularly
- Tune batch sizes based on memory bandwidth
- Profile memory access patterns to reduce unnecessary data movement.
2. Storage and Data Pipeline Bottlenecks
GPUs are only as fast as the data they receive. This bottleneck can starve GPUs long before compute limits are reached.
Why this happens
- Slow storage read/write speeds
- Overloaded shared storage
- Weakly designed data ingestion pipelines
Why it matters
- Training delays
- Inconsistent job runtimes
How to fix it
- Set up multi-tier caching across RAM, SSD, and cold storage
- Continuously monitor latency and cache hit rates to catch performance drops
- Preprocess and cache training data instead of reloading raw datasets for every run.
- Design pipelines that stream data continuously to GPUs rather than loading in bursts.
3. GPU Utilization vs Throughput Gap
High GPU utilization does not always mean real progress. GPUs appear busy while still delivering poor throughput because they spend time waiting on data, memory, or synchronization.
Why this happens
- GPU scheduling inefficiencies
- Poor workload distribution across GPUs
- Synchronization delays between tasks
Why it matters
- Expensive GPUs deliver low real output
How to fix it
- Monitor utilization against throughput metrics such as tokens/sec or samples/sec
- Reduce synchronization overhead with better batching and pipeline parallelism
- Use workload-aware schedulers that align GPU allocation with model size and batch patterns.
- Enable GPU sharing or MIG for smaller or bursty jobs.
4. Power and Thermal Constraints
Power and cooling constraints are silent performance killers. According to IEA report 2025, global electricity consumption for data centers is expected to reach around 945 TWh by 2030. When systems overheat or hit power caps, GPUs throttle automatically.
Why this happens
- Insufficient power supply
- Inadequate cooling design
- Lack of thermal monitoring
- Dense GPU deployments without airflow planning
Why this matters
- Gradual performance degradation
- Sustainability Pressure
- Grid lead times for new interconnects
How to fix it
- Use carbon-aware orchestration to shift workloads based on energy availability.
- Adopt closed-loop liquid cooling systems.
- Improve cooling layouts before scaling AI infrastructure.
- Monitor clock speeds alongside temperature and power draw.
- Schedule intensive training jobs during off-peak power usage when possible.
5. Training vs Inference Infrastructure Scaling
Training and inference stress your infrastructure differently. These GPU bottlenecks in AI training vs inference directly impact production reliability.
Why this happens
- Training prioritizes throughput, while inference prioritizes low latency
- Shared infrastructure creates contention
- Cache fragmentation
- Tokenizer overload
Why this matters
- Model deployment latency and GPU swaps
- Generate AI infrastructure waste
- Inconsistent inference performance
How to fix it
- Enable continuous batching and speculative decoding
- Use high-performance attention kernels
- Constrain context window sizes or offload them to paged memory when possible
6. Orchestration and AI Observability Gaps
Without clear visibility, bottlenecks remain hidden until AI cost overruns or deadlines slip.
Why this happens
- Limited visibility into GPU, network, and storage metrics
- Disconnected monitoring tools
- Weak AI workload orchestration
Why this matters
- Delayed issue detection
- Underutilized GPU clusters
- Reduced AI infrastructure resiliency
How to fix it
- Use integrated dashboards to detect anomalies and trigger automated scaling before performance degradation begins.
- Standardize environments to reduce setup delays between runs.
- Kill stalled or low-priority jobs automatically to free resources.
Insights into the Most Overlooked AI Infrastructure Bottleneck
As AI models scale, networks came up as one of the major AI infrastructure bottlenecks. Since more accelerators are added, the network stops being a supporting layer in the infrastructure. Instead, it decides the outcome:
- If the network is slow or congested, it limits AI performance. In this case, the network becomes a bottleneck.
- If the network is high-bandwidth, low-latency, and well-optimized, it unlocks full accelerator performance. Here, the network becomes a breakthrough.
A global survey conducted by Heavy Reading in collaboration with Keysight Technologies highlights this shift. 55% of respondents are using 400G networks, while 22% are already trialing 1.6T speeds. This bandwidth demand shows how network performance is central to AI scalability.
How to Optimize the Network Performance in AI Infrastructure?
According to Keyinsights, organizations are adopting the following options to address AI networking challenges.
Ethernet-based Architectures
To manage networks, Ethernet fabrics like Software Defined Networking (61%), Ultra-Ethernet (58%), Ethernet/RoCEv2 (49%), and InfiniBand/NVLink (38%) are considered. Despite its widespread adoption, SDN still operates on conventional Ethernet assumptions.
The Ultra Ethernet, on the other hand, is built for AI and high-performance computing. It redesigns the protocol stack to offer precision, speed, and scalability for AI workloads.
Advanced Emulators
Emulators help expose issues in latency, bandwidth, congestion, and synchronization by reproducing real-world AI traffic patterns. It also enables safe experimentation without risking production clusters and supports optimization without immediate hardware investment. This maximizes existing infrastructure while guiding future AI network scaling decisions.
9 Best Practices for AI Infrastructure Optimization
Here are best practices to remove AI bottlenecks and improve AI workload performance:
- Avoid idle GPU capacity by using efficient scheduling, right-sizing clusters, and matching workloads to the correct accelerator type.
- Ensure fast data ingestion and preprocessing so GPUs never wait on data.
- Use high-bandwidth and low-latency networking to prevent slowdowns during distributed training.
- Adopt AI-optimized validation tools to emulate large-scale AI clusters before deployment.
- Optimize inter-node communication to avoid inference latency issues.
- Balance compute, memory, and storage components without overinvesting in GPUs.
- Track utilization, latency, and throughput in real time.
- Build infrastructure that scales horizontally without re-architecting.
- Apply AI-specific security controls that protect data and models.
Optimized AI Infrastructure with Aptly Technology
Having an AI-ready infrastructure is not an advantage, but a requirement for innovation and growth. Aptly technology, a Microsoft Gold Partner, helps improve enterprise AI infrastructure by delivering end-to-end scalable, secure, and performance-optimized solutions.
Why Choose Aptly for AI Infrastructure?
Aptly brings deeps technical expertise and practical experience in building and managing large-scale AI infrastructures, including GPU clusters and high-performance compute environments.
Whether on-premises, cloud-based, or hybrid, Aptly ensures your infrastructure is built to support demanding AI and ML workloads with maximum efficiency.
Core Capabilities that Drive Value
- AI Infrastructure Modernization: Aptly modernizes traditional IT stacks to become AI-ready. This is done by integrating cutting-edge hardware such as GPUs and TPUs, advanced networking, and scalable architecture.
- AI Cluster Provisioning: Designing and provisioning AI clusters is complex. Aptly’s team assesses compute needs, configures hardware accelerators, and establishes high-speed networking in your own data centers.
- Networking: Aptly offer AI networking solutions to reduce downtime and improve performance through automation and proactive insights.
- Robust Security: AI environments have unique security challenges. With Aptly, you can implement AI-specific security measures.
- Continuous Optimization and Monitoring: The AI world evolve, so should your infrastructure be improved. Aptly monitors performance, identifies bottlenecks, tracks utilization, and dynamically optimizes resource allocation to ensure peak performance without unnecessary cost.
- Scalability and Future-Proof Architecture: With Aptly, your infrastructure is designed to grow with your business. Flexible frameworks ensure you can respond quickly to new AI initiatives and market shifts.
What Makes Aptly Different?
- Accelerated innovation
- Cost efficiency
- Market agility
- Flexible infrastructure framework
- Trusted expertise
- 24/7 monitoring and support
FAQs
Q. What are the biggest bottlenecks in AI infrastructure?
The biggest bottlenecks include GPU underutilization, memory bandwidth limits, storage I/O delays, and network congestion. These issues slow training, increase latency, and reduce throughput.
Q. How AI workloads overload infrastructure?
AI workloads demand high compute, memory, and storage simultaneously. This overload leads to idle GPUs, throttled performance, and delayed model training or inference.
Q. What is the most overlooked AI infrastructure bottleneck?
Network congestion. It slows data transfer between GPUs, storage, and nodes.
Q. How to fix AI infrastructure bottlenecks at scale?
Proactive monitoring, workload optimization, and proper cluster sizing help avoid bottlenecks. Using specialized AI infrastructure management, like Aptly Technology, ensures resources are fully used.
Q. Why do some AI projects fail despite having top-tier hardware?
Due to poor orchestration, suboptimal scheduling, or network limitations can delay performance. Effective infrastructure management is key to turning hardware potential into results.
Q. What causes GPU underutilization in AI infrastructure?
GPU underutilization happens when data pipelines, memory bandwidth, networking, or orchestration cannot feed GPUs quickly. Weak workload scheduling and I/O bottlenecks also leave GPUs idle despite available capacity.
Conclusion
Tackling AI infrastructure bottlenecks and optimizing your data center is essential to unlock peak performance, reduce AI infrastructure challenges, and scale efficiently.
With Aptly technology’s expertise in managing and optimizing AI workloads, your enterprise can achieve faster, more reliable, and cost-effective AI operations.
Crush AI bottlenecks and accelerate your AI workloads with Aptly’s optimized infrastructure.